Understanding Angiography
Angiography is a medical imaging technique that involves the injection of a contrast dye into the blood vessels to create detailed images of the vascular system.
Definition and Types:
Angiography can be performed using different modalities:
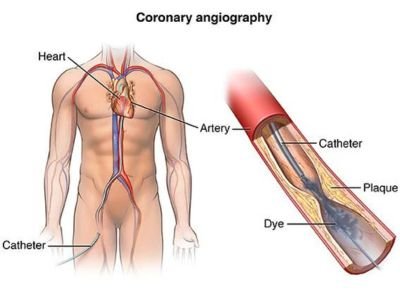
- Conventional Angiography: This technique involves the insertion of a catheter into a blood vessel and the injection of a contrast dye to visualize the vessels on X-ray images.
- CT Angiography (CTA): CTA utilizes computed tomography technology to generate three-dimensional images of the blood vessels after the injection of a contrast dye.
- Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA): MRA uses magnetic resonance imaging to create detailed images of blood vessels without the need for X-rays or contrast dyes.
Indications and Uses:
Angiography is used to diagnose and evaluate various vascular conditions, including:
- Arterial blockages or narrowing
- Aneurysms (weakened and bulging areas in blood vessels)
- Vascular malformations
- Tumors affecting blood vessels
- Peripheral artery disease
- Stroke or transient ischemic attacks (TIAs)
- Renal artery disease
- Coronary artery disease
The Angiography Procedure
Understanding the angiography procedure and what to expect during the process is crucial for informed decision-making and optimal outcomes.
Pre-procedure Preparation:
Before angiography, a comprehensive evaluation is conducted, including a review of medical history, physical examination, and relevant diagnostic tests to assess the patient's vascular health.
The Procedure:
The angiography procedure typically involves the following steps:
- Anesthesia: Depending on the specific case, local anesthesia or conscious sedation may be administered to keep the patient comfortable during the procedure.
- Catheter Insertion: A catheter is inserted into a blood vessel, usually in the groin or arm, and guided to the target area of examination.
- Contrast Dye Injection: A contrast dye is injected through the catheter to make the blood vessels visible on the imaging study.
- Image Acquisition: X-ray, CT, or MRI equipment is used to capture detailed images of the blood vessels as the contrast dye flows through them.
- Post-procedure Care: After the procedure, the catheter is removed, and pressure is applied to the insertion site to prevent bleeding. The patient is monitored for a short period to ensure stability before being discharged or transferred to a recovery area.
Benefits and Risks of Angiography
Understanding the benefits and potential risks associated with angiography is important for making informed decisions and managing expectations.
Benefits of Angiography:
Angiography offers several advantages:
- Accurate Diagnosis: Angiography provides detailed images of blood vessels, enabling accurate diagnosis and evaluation of various vascular conditions.
- Guiding Treatment: Angiography helps guide treatment decisions, such as the need for surgical intervention, stent placement, or embolization procedures.
- Minimally Invasive: Many angiography techniques are minimally invasive, involving small incisions and shorter recovery times compared to traditional surgery.
Risks and Complications:
While angiography is generally safe, there are some risks and potential complications to be aware of:
- Allergic Reactions: Some patients may experience an allergic reaction to the contrast dye, although this is rare.
- Bleeding or Hematoma: There is a small risk of bleeding or hematoma at the catheter insertion site.
- Blood Vessel Damage: In rare cases, the blood vessel may be damaged during the catheter insertion process.
- Radiation Exposure: Conventional angiography involves X-ray imaging, which exposes the patient to a small amount of radiation. However, modern techniques minimize radiation exposure as much as possible.
Recovery and Follow-up Care
After angiography, proper recovery and follow-up care are essential for optimal healing and outcomes.
Post-procedure Recovery:
Following angiography, patients may need to stay in a recovery area for a brief period to ensure stability. The insertion site is monitored for bleeding or complications, and pressure is applied to promote clotting.
Activity Restrictions:
Patients are typically advised to avoid strenuous activities, lifting heavy objects, or engaging in vigorous exercises for a specified period following the procedure. It is essential to follow the healthcare provider's instructions regarding activity restrictions and wound care.
Follow-up Appointment:
A follow-up appointment is scheduled to review the angiography results, discuss the diagnosis, and determine the appropriate treatment plan based on the findings. The healthcare provider will provide guidance on any necessary lifestyle modifications or further interventions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Seeking Expert Vascular Care
At
VascularHyd, we specialize in angiography procedures. Dr. Rahul Agarwal and our experienced team are dedicated to providing personalized care and accurate diagnoses through advanced imaging techniques.
Why Choose VascularHyd?
- Expertise in angiography and vascular imaging
- State-of-the-art facilities and advanced imaging technologies
- Highly skilled vascular surgeons and medical professionals
- Patient-centered care and comprehensive evaluation
- Timely and accurate diagnosis for effective treatment planning
Contact us today to schedule a consultation and discuss your angiography concerns or to learn more about our vascular services