Welcome to
VascularHyd, your trusted source for information about vascular diseases. In this article, we will explore thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS), a condition that involves compression of nerves or blood vessels in the thoracic outlet area. Dr. Rahul Agarwal, a leading vascular surgeon, specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of thoracic outlet syndrome. Whether you are seeking knowledge or require expert care, you have come to the right place.
Understanding Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
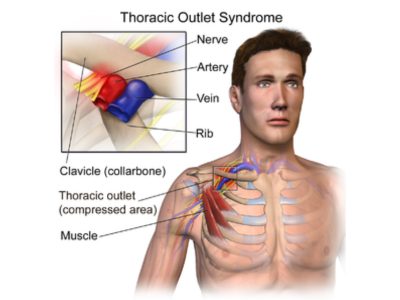
Thoracic outlet syndrome refers to a group of disorders characterized by compression of nerves or blood vessels in the thoracic outlet, which is the space between the base of the neck and the armpit.
Definition and Types:
Thoracic outlet syndrome can be classified into three types:
- Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: This type involves compression of the brachial plexus, a network of nerves that control the movement and sensation of the upper extremity.
- Vascular Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: This type involves compression of the blood vessels, such as the subclavian artery or subclavian vein, leading to compromised blood flow or venous drainage.
- Nonspecific Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: This type includes cases where the exact cause of compression is unclear or involves a combination of nerve and vascular compression.
Causes and Risk Factors:
Several factors can contribute to the development of thoracic outlet syndrome, including:
- Anatomical variations, such as an extra rib (cervical rib) or an abnormal fibrous band
- Poor posture, especially with rounded shoulders and forward head position
- Repetitive arm movements or activities, such as typing, overhead lifting, or sports involving repetitive arm motion
- Trauma, such as whiplash injuries or fractures
- Enlarged muscles or muscle abnormalities
- Certain medical conditions, including cervical disc disease, tumors, or connective tissue disorders
Symptoms of Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
The symptoms of thoracic outlet syndrome can vary depending on the type and location of compression.
Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome:
Neurogenic thoracic outlet syndrome typically presents with symptoms such as:
- Pain or aching in the neck, shoulder, and upper extremity, which may radiate to the hand or fingers
- Numbness or tingling in the arm, hand, or fingers
- Weakness or fatigue in the affected arm or hand
- Muscle wasting or atrophy in severe cases
Vascular Thoracic Outlet Syndrome:
Vascular thoracic outlet syndrome may cause symptoms such as:
- Swelling, discoloration, or coolness of the hand or arm
- Pain or aching in the arm, especially with arm elevation or exertion
- Weakened or absent pulses in the affected arm
- Blood clot formation (thrombosis) in rare cases
Diagnosing Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
Accurate diagnosis of thoracic outlet syndrome involves a comprehensive evaluation and diagnostic tests.
Medical History and Physical Examination:
A detailed medical history is obtained to understand the patient's symptoms, medical conditions, and potential risk factors. During the physical examination, the healthcare provider evaluates the patient's posture, range of motion, and performs specific tests to reproduce symptoms.
Imaging Tests:
Imaging techniques such as X-ray, MRI, or CT scan may be used to visualize the structures of the thoracic outlet area and identify any anatomical variations, abnormalities, or bony abnormalities such as cervical ribs.
Nerve Conduction Studies and Electromyography:
These tests assess nerve function and help determine if there is nerve compression or damage in the thoracic outlet area. Nerve conduction studies measure the speed and strength of electrical signals traveling along the nerves, while electromyography records electrical activity in the muscles.
Treatment Options for Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
Treatment for thoracic outlet syndrome aims to relieve symptoms, reduce compression, and improve function.
Non-Surgical Approaches:
Non-surgical treatments are often the first line of management and may include:
- Physical therapy: A physical therapist designs a customized exercise program to improve posture, strengthen muscles, and alleviate compression on nerves or blood vessels.
- Pain management techniques: This may involve the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants, or nerve pain medications to alleviate pain and discomfort.
- Ergonomic modifications: Education on proper ergonomics and posture, especially during work or activities that may contribute to thoracic outlet syndrome.
- Lifestyle changes: Recommendations to avoid activities that exacerbate symptoms, such as repetitive arm movements or heavy lift
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation:
Physical therapy plays a vital role in the management of thoracic outlet syndrome. It includes:
- Stretching exercises: Specific stretching routines to improve flexibility and relieve muscle tension in the neck, shoulder, and upper extremit
- Strengthening exercises: Targeted exercises to strengthen the muscles around the shoulder girdle, improving stability and reducing compression on the thoracic out
- Postural training: Techniques to improve posture and body mechanics to minimize strain on the nerves and blood vessels in the thoracic out
Surgical Intervention:
Surgical intervention may be considered in severe cases or when conservative treatments fail to provide relief. The goal of surgery is to relieve compression on the affected structures, and the specific procedure depends on the underlying cause and type of thoracic outlet syndrome. Surgical options may include:
- First rib resection: Removal of an extra rib or a portion of the first rib to alleviate compression.
- Scalene muscle release: Release of the scalene muscles to reduce their tension and improve blood flow and nerve function.
- Vascular bypass: In cases of vascular thoracic outlet syndrome, bypass surgery may be performed to redirect blood flow around the compressed or blocked vessel.
Lifestyle Modifications and Self-Care
Adopting certain lifestyle modifications and practicing self-care can help manage thoracic outlet syndrome and prevent symptom recurrence.
Post-Treatment Care:
Following treatment, adherence to post-treatment care is essential for optimal recovery. This may include:
- Regular follow-up visits with the healthcare provider to monitor progress and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
- Compliance with prescribed medications and exercises as advised by the healthcare provider.
- Communication with the healthcare provider regarding any changes in symptoms or concerns.
Ergonomics and Posture:
Practicing good ergonomics and maintaining proper posture during daily activities can help alleviate symptoms and reduce strain on the thoracic outlet area. Recommendations may include:
- Using ergonomic chairs and supportive cushions to maintain a neutral spine position.
- Adjusting computer screens and workstations to minimize strain on the neck and shoulders.
- Taking frequent breaks during repetitive activities to avoid prolonged postures.
Strengthening Exercises and Stretching:
Engaging in specific strengthening exercises and stretching routines
can help improve muscle balance, flexibility, and overall strength. These exercises are tailored to target the muscles and structures involved in thoracic outlet syndrome and may include:
- Shoulder blade squeezes to strengthen the muscles between the shoulder blades.
- Neck stretches and range-of-motion exercises to improve flexibility and relieve muscle tension.
- Upper extremity exercises using resistance bands or light weights to enhance muscle strength and stability.
Frequently asked questions
Seeking Expert Vascular Care
At VascularHyd, we specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of thoracic outlet syndrome. Under the expertise of Dr. Rahul Agarwal, our team is dedicated to providing personalized care and tailored treatment plans.
Why Choose VascularHyd?
- Expertise in thoracic outlet syndrome diagnosis and treatment
- State-of-the-art facilities and advanced imaging technologies
- Highly skilled vascular surgeons and medical professionals
- Patient-centered care and individualized treatment plans
- Comprehensive post-treatment care and follow-up
Contact us today to schedule a consultation and discuss your thoracic outlet syndrome concerns.