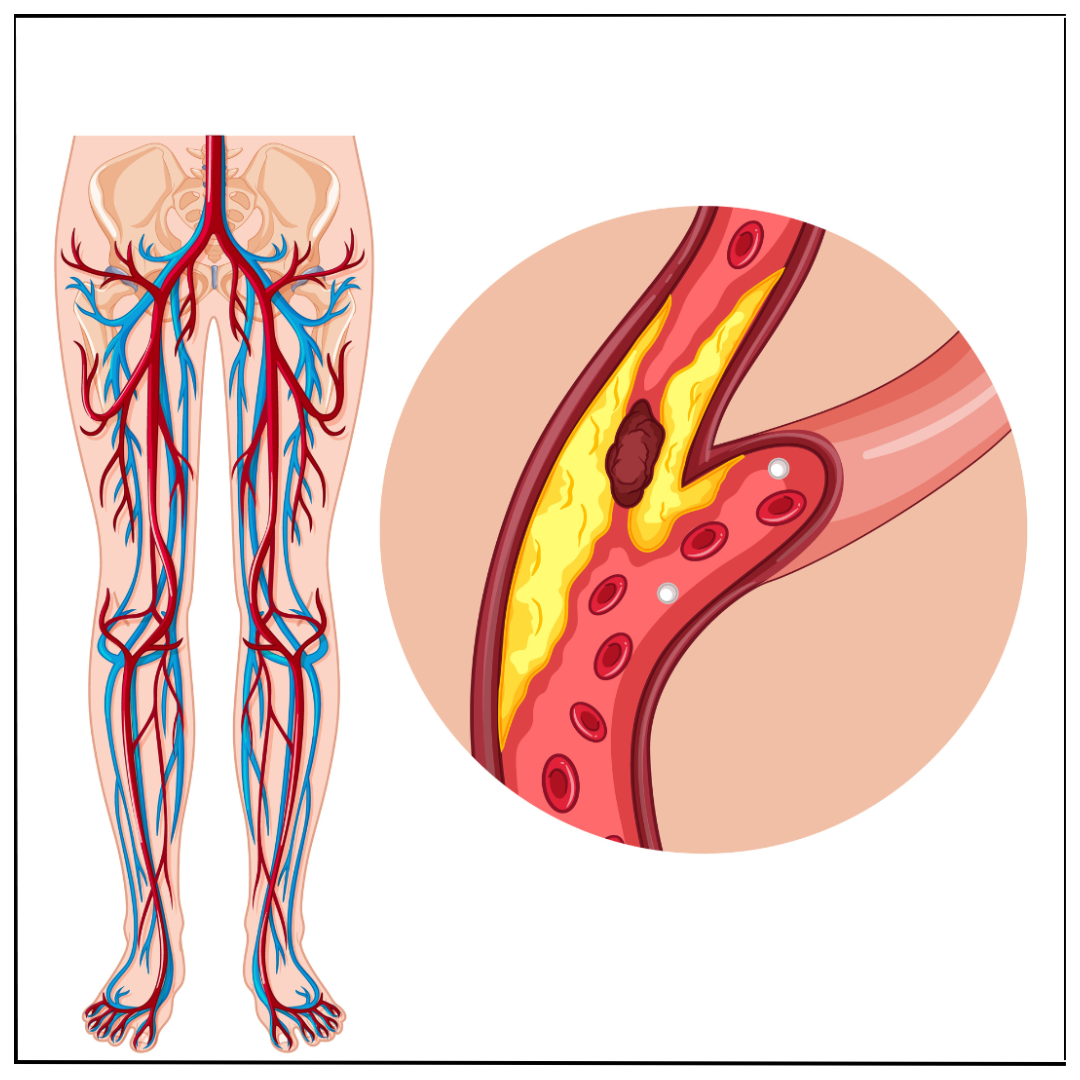
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a condition where a blood clot forms in the deep veins, most often in the legs. It is a serious health issue that requires timely diagnosis and treatment. If untreated, it can lead to pulmonary embolism (PE) — a potentially life-threatening condition where a clot travels to the lungs.
Causes of DVT
DVT occurs when blood flow slows down, veins are injured, or the blood has an increased tendency to clot. Common causes include:
- Prolonged immobility: Long flights, car rides, or bed rest after surgery or illness.
- Injury to a vein: Surgery, trauma, or vein inflammation.
- Increased clotting tendency: Medical conditions, medications, or genetic factors.
- Pregnancy & postpartum period: Hormonal changes and pressure on pelvic veins.
- Age: Risk increases after 40.
- Other factors: Obesity, smoking, cancer, or previous clot history.
Recognizing these risk factors can help in early prevention.
Symptoms of DVT
Sometimes DVT develops without obvious warning signs. However, common symptoms include:
- Swelling in one leg (calf or thigh).
- Pain or tenderness in the leg, often resembling cramps.
- Warmth in the affected area compared to the other leg.
- Red or darkened skin over the clot area.
- Enlarged visible veins.
?? If you notice these signs, seek medical help immediately.
Why Is DVT Dangerous?
DVT is dangerous because clots can break loose and travel through the bloodstream. This can lead to:
- Pulmonary Embolism (PE): A clot in the lungs causing chest pain, breathlessness, or collapse.
- Post-thrombotic syndrome: Long-term swelling, pain, and skin changes in the affected leg.
- Recurrent DVT: Higher risk of developing future clots.
Early treatment significantly reduces these risks.
How Is DVT Diagnosed?
Diagnosis requires a clinical examination and specialized tests, including:
- Ultrasound Doppler: Safe, painless scan to detect clots.
- Blood test (D-dimer): Checks for clot breakdown products.
- Other imaging (Venography, CT, MRI): Used in selected cases.
A vascular specialist combines symptoms, risk factors, and test results to confirm the diagnosis.
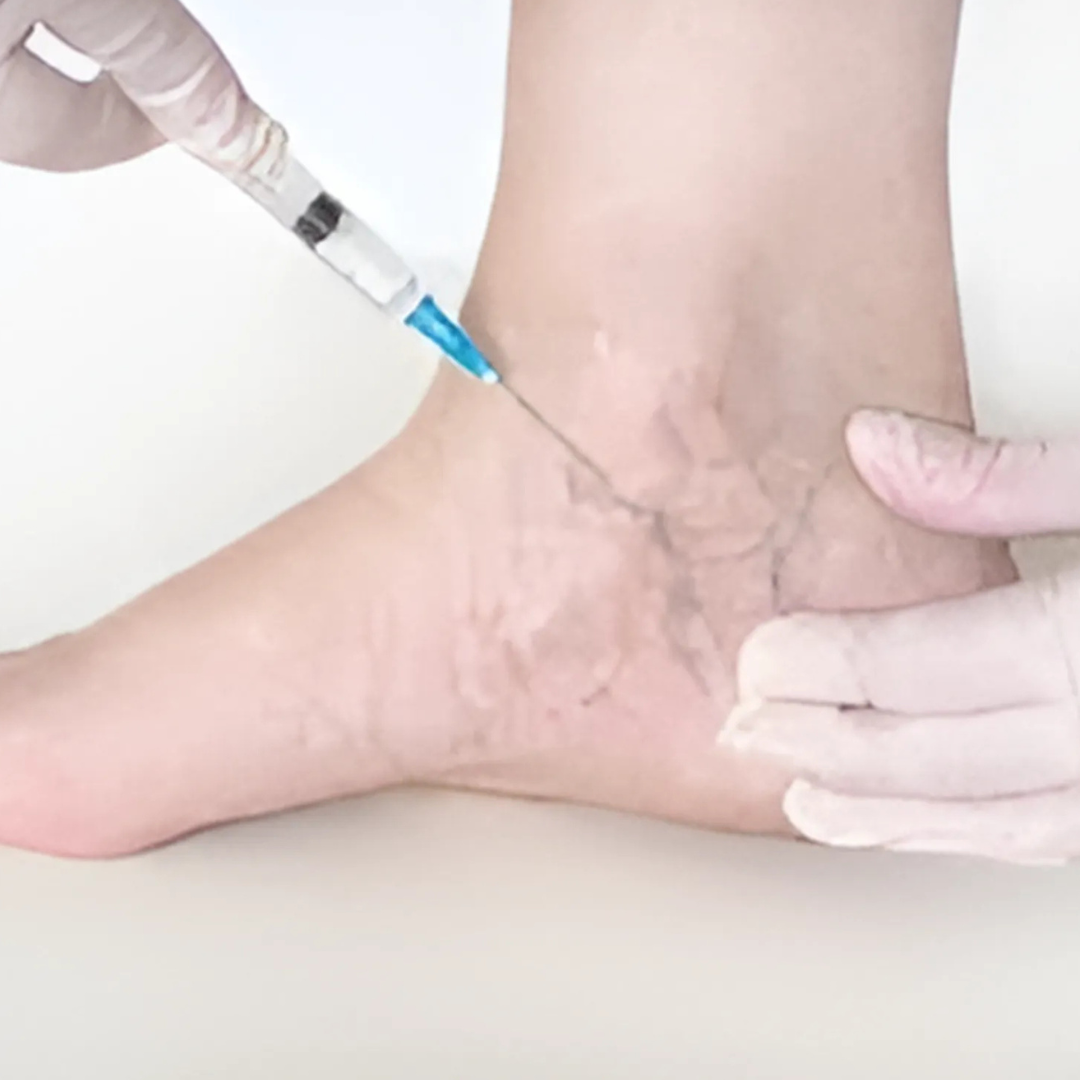
Treatment for Deep Vein Thrombosis
Treatment goals are to prevent the clot from growing, relieve symptoms, and avoid complications. Options include:
- Blood thinners (anticoagulants): Most common treatment to stop clot growth.
- Compression stockings: Improve circulation and reduce swelling.
- Thrombolytic therapy: Medicines to dissolve clots in severe cases.
- Surgical options: Rarely, clot removal or a filter in the vein may be required.
Every treatment plan is tailored to the patient’s health, clot size, and risk level.
Preventing DVT: Everyday Tips
Simple lifestyle steps can lower your risk:
- Stay active and avoid sitting for long periods.
- Take walking/stretching breaks during travel.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Quit smoking.
- Use compression stockings if advised.
- Follow your doctor’s instructions after surgery or hospitalization.
When to Consult a Specialist
If you suspect DVT, do not delay. Timely care can save lives and prevent complications.
? Consult Dr. Rahul Agarwal at VascularHYD, Hyderabad — a trusted vascular and endovascular specialist. With advanced diagnostic tools and personalized treatments, you receive world-class care close to home.
? Remember: DVT is preventable and treatable when diagnosed early. Awareness and quick action make all the difference.
 What You Need to Know.jpg)





.png)
 (1).png)